Offers a comprehensive guide to implementing automated testing. It covers the technology stack with a focus on JavaScript/TypeScript and the Playwright testing framework, including API generation and project structure. It explains how to use Playwright fixtures, how to customize them, and why. It provides practical advice on writing different types of test cases. These include general, E2E, and API tests. Reporting is covered with an overview and details of custom Playwright reporters, summarised reporting, and integrating with TestRail. The article also discusses the setup for nightly and manual testing on CircleCI, and concludes with plans for the future development of features in the test automation area.
Table of contents
- Tech stack overview
1.1. Language stack: Javascript/Typescript
1.2. Testing framework: Playwright
1.2.1. What Playwright?
1.2.2. Why Playwright?
1.2.3. Playwright limitations
1.3. API Generator
1.3.1. Why API Generator?
1.3.2. How to generate API
1.4. Folder structure
1.4.1. Project structure
1.4.2. A testing app structure - Playwright Fixtures
2.1. What are Test fixtures?
2.2. Why fixtures?
2.2.1. Built-in fixtures
2.3. Custom fixtures - How to write test case
3.1. Aliases
3.2. Common test cases
3.2.1. Conventions
3.2.2. Test script structure
3.3. E2E test cases
3.4. API test cases - Reports
4.1. Report overview
4.2. Custom reporter for Playwright
4.3. Summary Reporter
4.4. TestRail Reporter - Nightly and manual test on CircleCI
5.1. Nightly test
5.2. Manual test - Feature plans
1. Tech stack overview
1.1. Language stack: Javascript/Typescript
- Using TypeScript for strong type and reducing wrong attributes
- Node package management tool: Yarn
- Code lint: EsLint (simple-import-sort + prettier + …)
1.2. Testing framework: Playwright
1.2.1. What is Playwright?
- Cross-browser. Playwright supports all modern rendering engines including Chromium, WebKit, and Firefox.
- Cross-platform. Test on Windows, Linux, and macOS, locally or on CI, headless or headed.
- Cross-language. Use the Playwright API in TypeScript, JavaScript, Python, .NET, Java.
- Test Mobile Web. Native mobile emulation of Google Chrome for Android and Mobile Safari. The same rendering engine works on your Desktop and in the Cloud.
1.2.2. Why Playwright?
- Supports multiple languages including JavaScript/TypeScript, Java, .NET, Python
- It supports multi-tab, multi-user, and iframe test cases.
- It is available as a VS Code extension with one-click-to-run tests and includes step-by-step debugging, selector exploration, and logging of new tests.
- It supports different types of testing, such as end-to-end, functional, and API testing.
- Supports automated accessibility testing with third-party plugins.
- It provides various debugging options like Playwright Inspector, Browser Developer Tools, VSCode Debugger, and Monitor Viewer Console Logs.
- It has built-in reporters like JSON, JUnit, and HTML Reporter. You can also create custom reports using Playwright
- Faster and more reliable than Cypress. There are a lot of online articles or topics that mention the unreliable of Cypress without a resolved solution:
- Cypress hanging on circleCI but pass locally
- Cypress Testing: stuck at wait-on http://localhost:3000
- Cypress Testing: stuck at wait-on http://localhost:3000 (StackOverflow)
- Cypress sometimes stalls/hangs with no output when running in Jenkins with Docker
- CYPRESS tests pass locally but are hanging on circleCI
- Cypress hung up trying to run a spec – won’t resolve
- Cypress unexpectedly and randomly hangs when running tests in CI
1.2.3. Playwright limitations
- Does not support Microsoft Edge or earlier IE11.
- Uses a desktop browser instead of a real device to emulate a mobile device
1.3. API Generator
1.3.1. Why API Generator?
- Consume API is very clear and simple via classes and methods
- Don’t need any further confirmation between BE, FE and QA
Example:
// File: without_api_generator.ts
test('Test case 1', async ({ request }) => {
const newIssue = await request.post(`/repos/github-username/test-repo-1/issues`, {
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/vnd.github.v3+json',
// Add GitHub personal access token.
'Authorization': `token ${process.env.API_TOKEN}`,
},
data: {
title: '[Bug] report 1',
body: 'Bug description',
},
})
expect(newIssue.ok()).toBeTruthy()
const issues = await request.get(`/repos/github-username/test-repo-1/issues`, {
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/vnd.github.v3+json',
// Add GitHub personal access token.
'Authorization': `token ${process.env.API_TOKEN}`,
},
})
expect(issues.ok()).toBeTruthy()
expect(await issues.json()).toContainEqual(expect.objectContaining({
title: '[Bug] report 1',
body: 'Bug description',
}))
})// File: with_api_generator.ts
test('Test case 1', async ({ githubClient }) => {
const newIssue = await githubClient.createIssue({
data: {
title: '[Bug] report 1',
body: 'Bug description',
},
})
expect(newIssue.ok()).toBeTruthy()
const issues = await githubClient.getIssues()
expect(issues.ok()).toBeTruthy()
expect(await issues.json()).toContainEqual(expect.objectContaining({
title: '[Bug] report 1',
body: 'Bug description',
}))
})1.3.2. How to generate API
- BE will generate
swagger.jsonbased-on services’ implementation - FE will generate API services from
swagger.jsonvia using swagger-typescript-api:- Overwrite
http-client.etato useAPIContextRequestof Playwright instead offetch
- Overwrite
1.4. Folder structure
- Folder structure follows monorepo architecture (Turborepo)
1.4.1. Project structure
.circlecicontains CircleCI config filesappscontains testing appspackagescontains common packages which are used in testing appcommon-toolscontains code for common tools which will be used in testing apps. Example:gen-open-api,unify-test-case, etc…eslint-config-customcontains base configuration for EsLintplaywright-commoncontains common components, pages, types, and utils which are used in test cases, fixtures, etc…summary-reportis a customer report to count total passed, failed, flaky, skipped, timed out, or interrupted. Is used for Slack notificationtsconfigcontains base configuration for Typescript
.editorconfigdefines coding styles for multiple developers working on the same project across various editors and IDEs.eslintrc.jsis EsLint root config.gitignorecontains GIT ignored file list.npmrcstores the feed URLs and credentials that Npm uses.prettierignoreand.prettierrccontains configuration for prettier (Code Formatter)package.jsoncontains package information such as name, version, dependencies, scripts, etc…README.mdturbo.jsoncontains configuration for Turborepoyarn.lockstores exactly which versions of each dependency were installed. More details at here
1.4.2. A testing app structure
__reportscontains testing reports including Playwright, Allure, etc…__resultscontains trace files which are used for Trace Viewerdatacontains data for testinglibscontains helpers to support testingapicontains helpers for API testingconstantscontains constantsfixturescontains test base for E2E and API testinguicontains helpers for E2E testingcomponentscontains components’ fixtures such asglobalHeader,sidebarMenu, etc…pagescontains pages’ fixtures such asloginPage,switchOfficePage,createOfficePage, etc…
sql-scriptscontains SQL scripts which are used for setup and teardown of testingutilscontains utilities
testscontains all test casestoolscontains utility tools which not belong to helpers. Example:gen-open-api,unify-test-case.env.examplecontains an example for.envfile.eslintrc.jscontains EsLint configurationglobal.setup.tscontains global setup for all test casesglobal.teardown.tscontains global teardown setup for all test casespackage.jsoncontains package information such as name, version, dependencies, scripts, etc…playwright.config.tscontains Playwright configurationtsconfig.jsoncontains Typescript configuration
2. Playwright Fixtures
2.1. What are Test fixtures?
- Used to establish an environment for each test, giving the test everything it needs and nothing else.
- Isolated between tests.
- With fixtures, you can group tests based on their meaning, instead of their common setup.
2.2. Why fixtures?
- Encapsulate setup and teardown in the same place so it is easier to write.
- Reusable between test files – you can define them once and use them in all your tests. That’s how Playwright’s built-in
pagefixture works. - On-demand – you can define as many fixtures as you’d like, and Playwright Test will set up only the ones needed by your test and nothing else.
- Composable – they can depend on each other to provide complex behaviors.
- Flexible – tests can use any combinations of the fixtures to tailor the precise environment they need, without affecting other tests.
- Simplify grouping – you no longer need to wrap tests in
describes that set up environment, and are free to group your tests by their meaning instead.
2.2.1. Built-in fixtures
| Fixture | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| page | Page | Isolated page for this test run. |
| context | BrowserContext | Isolated context for this test run. The page fixture belongs to this context as well. Learn how to configure context. |
| browser | Browser | Browsers are shared across tests to optimize resources. Learn how to configure browser. |
| browserName | string | The name of the browser currently running the test. Either chromium, firefox or webkit. |
| request | APIRequestContext | Isolated APIRequestContext instance for this test run. |
2.3. Custom fixtures
To create your own fixture, use test.extend() to create a new test object that will include it.
// File: my-fixtures.ts
import { test as base } from '@playwright/test'
import { TodoPage } from './todo-page'
import { SettingsPage } from './settings-page'
// Declare the types of your fixtures.
type MyFixtures = {
todoPage: TodoPage;
settingsPage: SettingsPage;
};
// Extend base test by providing "todoPage" and "settingsPage".
// This new "test" can be used in multiple test files, and each of them will get the fixtures.
export const test = base.extend<MyFixtures>({
todoPage: async ({ page }, use) => {
// Set up the fixture.
const todoPage = new TodoPage(page)
await todoPage.goto()
await todoPage.addToDo('item1')
await todoPage.addToDo('item2')
// Use the fixture value in the test.
await use(todoPage)
// Clean up the fixture.
await todoPage.removeAll()
},
settingsPage: async ({ page }, use) => {
await use(new SettingsPage(page))
},
})
export { expect } from '@playwright/test'3. How to write test case
3.1. Aliases
- Purpose: to make test script look similar with other test frameworks like Jest, Mocha, Jasmine, etc…
- Alias list:
describeis an alias of thetest.describeitis an alias oftestbeforeAllis an alias oftest.beforeAllbeforeEachis an alias oftest.beforeEachafterEachis an alias oftest.afterEachafterAllis an alias oftest.afterAll
3.2. Common test cases
3.2.1. Conventions
- File name must be in lowercase. Can be a test suite or test case code. Example
c12345.tsfor test case ands56789.tsfor test suite - Each test file must contain a TestRail link to the test case or test suite. Example (demo link, inaccessible):
// File: c57293.ts
// Link: https://moneyforwardvn.testrail.io/index.php?/cases/view/57293
..
it('C57293 Verify menu header after user logs on the SCI system successfully', async ({ globalHeader }) => {
...
})- Tip: Script
yarn unify-testcasecan help you:- Change your file name to be in lower-case
- Prepend TestRail link to test case based-on your file name
3.2.2. Test script structure
Structure of test case contains following factors:
describeortest.describeto declare test suiteitortestto declare testcasebeforeAllortest.beforeAllto declare setup step for test suitebeforeEachortest.beforeEachto declare setup step for each test caseafterEachortest.afterEachto declare teardown step for each test caseafterAllortest.afterAllto declare teardown step for test suite
3.3. E2E test cases
describe,it,beforeAll,beforeEach,afterEach,afterAllandexpectare imported from@/libs/fixtures/e2e- Available fixtures:
paginationinlineNotificationtoastglobalHeadersidebarMenuloginPageswitchOfficePagenewOfficePageemployeeListPageemployeeInvitePageemployeeDetailPageemailSettingPageemailTemplatePreviewPageemailTemplateEditPagesendPackageListPagecompanySettingPagesenderInformationPage
3.4. API test cases
describe,it,beforeAll,beforeEach,afterEach,afterAllandexpectare imported from@/libs/fixtures/api- Available fixtures:
apiClientmanageGroupClientsendInvoiceClientpublicLoginPage
4. Reports
4.1. Report overview
- Slack channel:
#sci_automation_test_notify - Report type:
- Daily: Every morning from Monday to Friday (GTM+7)
- Monthly: TBD
- Trigger type:
nightlyormanual - App name:
senderorreceiver - Testing type:
apiore2e - Report format
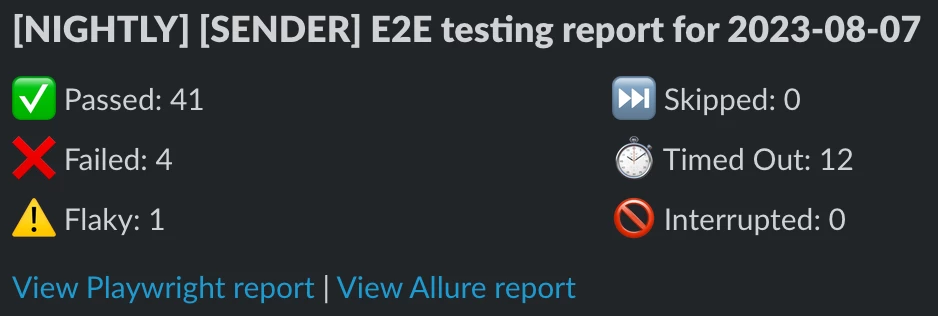
- Title:
[{TRIGGER_TYPE}] [{APP_NAME}] {TESTING_TYPE} testing report for {RUN_DATE} - Content:
- Total passed
- Total failed
- Total flaky
- Total skipped (due to depending on test case is failed)
- Total timed out (due to auto-waiting exceeding configured timeout)
- Total interrupted
- Example:
- Title:
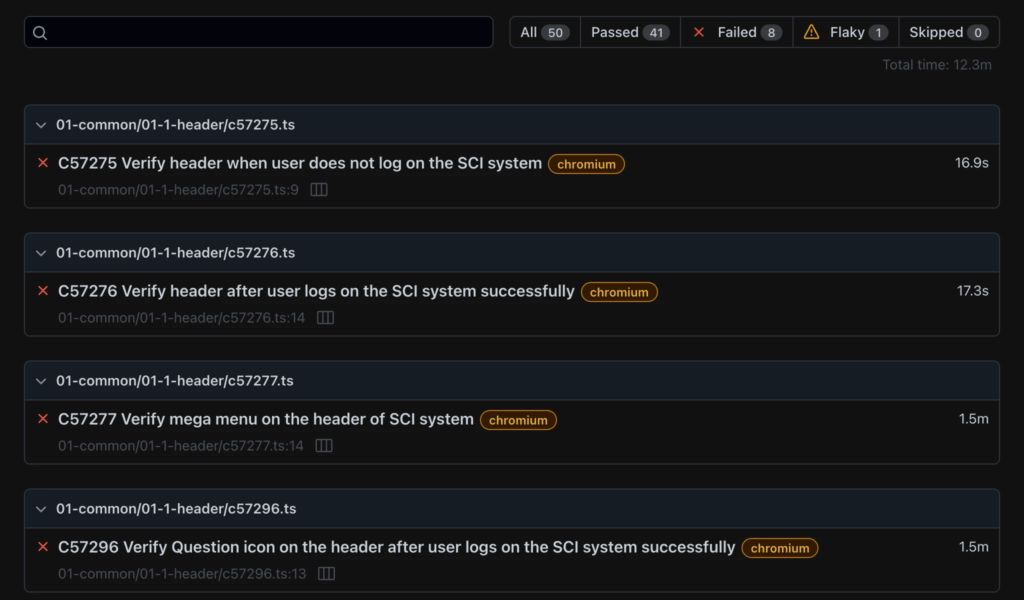
- Link to report detail
- Playwright report
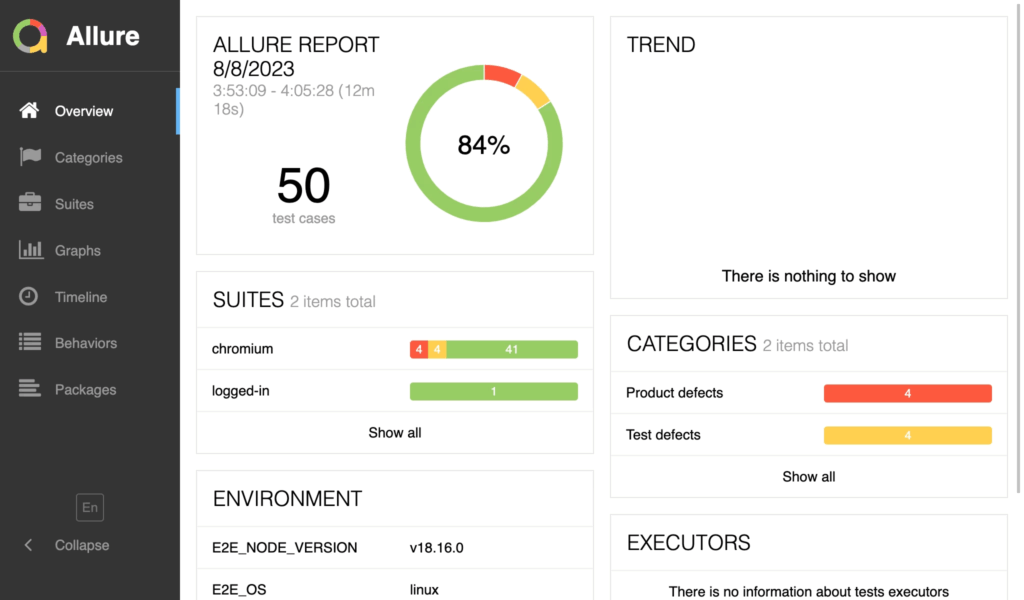
- Allure report
4.2. Custom reporter for Playwright
You can create a custom reporter by implementing a class with some of the reporter methods. Learn more about the Reporter API.
4.3. Summary Reporter
This report will calculate total passed, failed, flaky, skipped, timed-out and interrupted test cases as well as passed ratio and total duration. The result will be stored in JSON format
4.4. TestRail Reporter
This report will:
- Detect TestRail test cases’ id via test-case title
- Create
TestMilestonein the first day of a week (if does not exist) - Close
TestMilestonein the last day of a week (if does not close) - Create
TestRunwhenever running an Automation Test - Close
TestRunafter running the Automation Test - Create
TestResultfor all detected test cases
5. Nightly and manual test on CircleCI
Nightly and manual tests will run only on main branch
5.1. Nightly test
- Will test
apiande2efor all applications - Will be triggered at:
- With
UTCtimezone: 8:00 PM on Sunday, Monday-Thursday - With
GTM+7timezone: 3:00 AM on Monday-Friday
- With
- Scheduled trigger on CircleCI:
- Purpose: ensures that you catch such problems within 24 hours when they occur
5.2. Manual test
- Will be triggered manually when:
- Purpose: trigger
apiande2etesting for a specified application on demand
6. Feature plans
- Implement
Monthlyreport about detected bugs - Auto create JIRA ticket when finding bug after running Automation Test
- Generate test cases for testing type of parameters. Example:
username: stringparam will be tested with following input:null''!@#$%^&*()true123456789
